Starlink costs: What exactly is behind the service and how you can access it
Despite ongoing efforts and numerous promises, there are still gaps in network expansion. Rural regions in particular are lagging behind the expansion of nationwide broadband internet. A Starlink-style solution seems to be just what is needed at the moment. But what exactly can the service do? How high are the Starlink costs, where is the service available and what points speak against the project? In this feature, we reveal the most important key issues and go into detail.
What is Starlink?
No doubt some of you have heard this name more than once in the past few years. In short, Starlink is a satellite-based internet service launched by the private space company SpaceX. The aim is to provide broadband connections to all corners of the world via a large-scale fleet of mini-satellites.
Especially in regions that are currently poorly connected or not connected at all, the aim is to make it possible to access the Internet quickly, easily and independently of local conditions. Even data transfer to the North Pole is already possible in practice today.
With thousands of satellites operated from the US branch in Redmond, many countries around the globe are already covered. According to its own information, the service, which was launched in 2019, has a total of 2.2 million customers (as of the beginning of 2024), of which almost 60 percent are in the USA.
How does Starlink work?
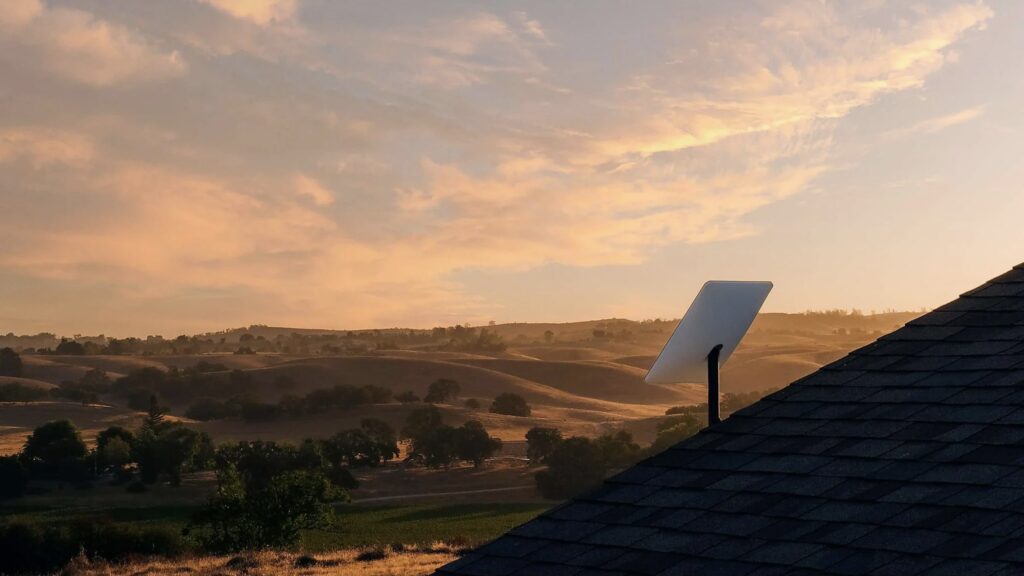

Starlink uses a network of over 5,700 satellites (as of January 2024), which are stationed in comparatively low earth orbits of around 330 to 370 and 500 to 620 kilometers. In relation to the total of around 7500 active satellites in space, the company currently provides a good three quarters of all satellites.
Due to its positioning close to the earth, the system achieves an internet connection with a reasonably low delay and higher data transfer rate. The Starlink satellites are connected to each other as well as to numerous ground stations on Earth.
For comparison: Geostationary satellites move at an altitude of around 36,000 kilometers above the equator, while the International Space Station hovers a good 400 kilometers above our atmosphere and is therefore surrounded by Starlink systems, so to speak.
Starlink costs: this is how much you pay
The pure subscription costs for private households are currently 120 dollars per month without a strict consumption limit and are therefore slightly above the level of well-known broadband providers, provided you assume an average speed of around 100 Mbit/s. On top of this, there are additional costs of 599 dollars for the peripherals and possibly additional costs for a suitable mount, which is provided in the store if you do not want to implement a DIY solution.

Calculated over an entire year, your monthly expenditure without an additional holder would be 170 dollars. Incidentally, the hardware can be rented for certain regions. If this option is available, you will be shown a corresponding option during the ordering process.
However, if you are not satisfied with the service, you can return the hardware within 30 days and receive a full refund. We have summarized all tariff models in the following overview.
Which subscription models does Starlink offer?
| Tariff | Standard | Priority | Mobile | Mobile Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly costs | $120 | From $140 | From $150 | From $250 |
| Special feature | No data limit with good latency | Public IP address incl. IPv6, prioritization in the network | No data limit in Germany, service in motion with a maximum speed of 16 km/h | No data limit, use on the move and at sea, prioritization in the network |
| Intended use | Private households | In companies and for users with high demand | In a motorhome or camper | For seafaring, emergency services and mobile businesses |
| Data volume | Unlimited | Unlimited 40 GB Priority | Unlimited domestically | Unlimited worldwide 50 GB Priority |
| Priority data | No | Yes, from 1 TB with extra costs | Yes, 50 GB with extra costs | Yes, from 1 TB with extra costs |
| Hardware costs | $599 | $2500 | $599 | $2500 |
| Router encryption | WPA2 | WPA2 | WPA2 | WPA2 |
What do I need for Starlink?
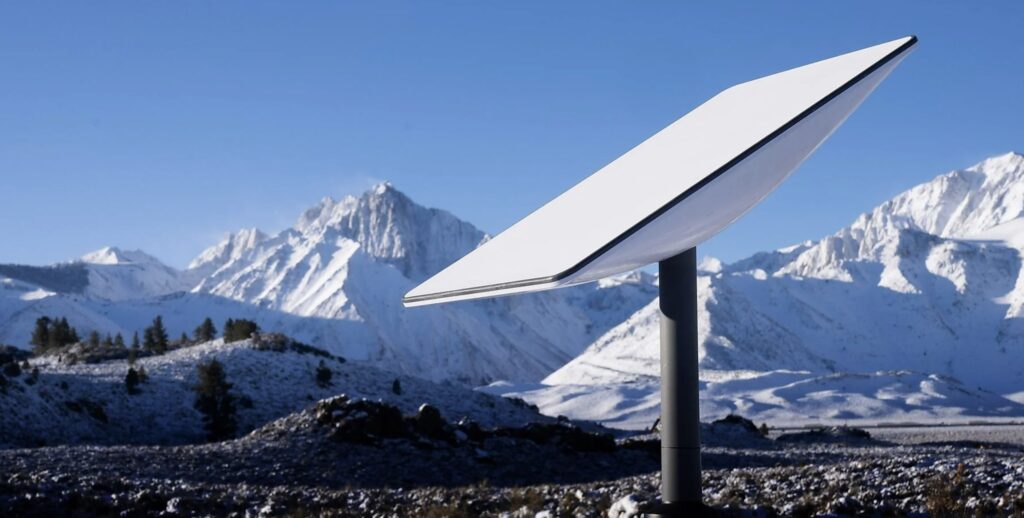
In addition to availability in your country, you need a paid subscription. From a technical point of view, some special equipment is required. Apart from a Wi-Fi router, a special receiver unit is required to retrieve the signal. The exact term for this is a “phased array” antenna.
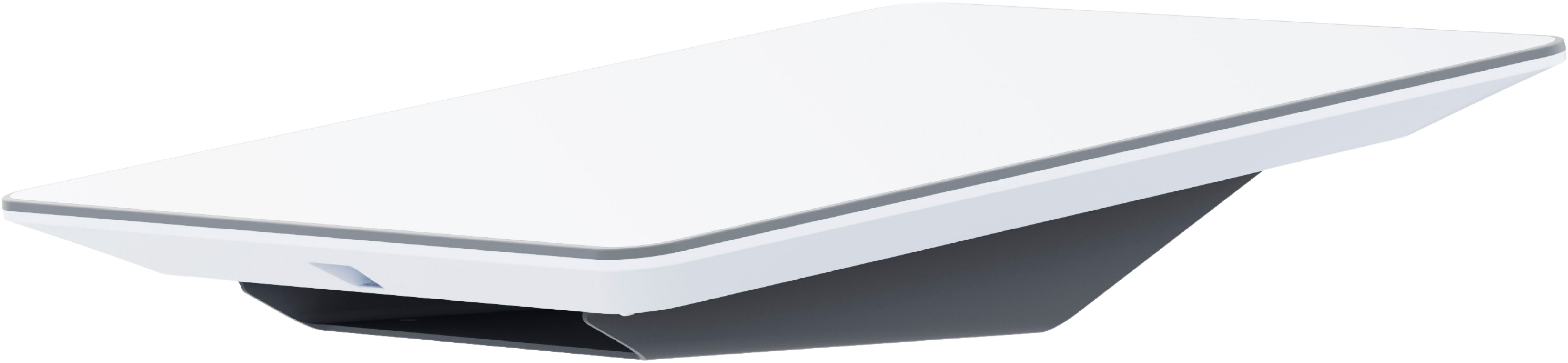

The special thing about this is that this device is able to automatically track the position of the satellites in space and adjust itself on this basis without the need for manual intervention. In addition, a snow melting function is now also integrated, which, according to Starlink, can independently remove a layer of up to 40 millimetres per hour. However, this does not save electricity. On the contrary: it can consume well over 100 watts of energy.
Caution: The view of the sky must always remain clear. For this purpose, Starlink provides you with an alignment tool via app to detect obstacles in order to achieve the best possible positioning on site. The program is available as an iOS and Android version. As long as there is no thick layer of ice on the receiving surface, the unit is largely weatherproof after commissioning.
Signal forwarding via WLAN router

Once the installation is complete, you can then tap into the connection as a Wi-Fi signal via a router. The connection options vary depending on the model generation. While the first router revision still has an Aux port, you will have to do without this interface on the second generation of devices. If you want to establish a wired connection to one or more devices, you will need an Ethernet adapter.
The Starlink Shop will provide you with one directly. In principle, however, adapters from third-party manufacturers should also do the job. Version three has two dedicated LAN interfaces on the back. Additional cable connections can be set up via a switch if necessary. All models also have dual band and the IEEE802.11ac standard.
Note: Although third-party devices are possible in principle, the company expressly points out that it cannot guarantee compatibility or performance with external equipment.
Where is Starlink available?

The service is currently available in over 60 countries worldwide (as of January 2024). These include large parts of North and South America, Europe and some regions in East Asia. Numerous countries are still on a waiting list and will also be connected in the coming years. In large parts of Africa and Asia in particular, there is still some catching up to do.
You can check the current availability yourself at any time using a dynamic world map. Nations such as Russia or China are not included here due to various factors. The Chinese government generally does not want to allow Starlink Internet. In Russia, the technology is not certified and therefore cannot be used.
How fast is Starlink?
The company does not specify any fixed download and upload rates in its offers. Instead, the service refers to possible speed ranges that make it difficult to give a general answer to this question. The fact is that your surfing speed generally depends on the number of active users and your chosen tariff model. Outside of peak times, you will therefore have more bandwidth available than at lunchtime, for example. You will also be given preferential treatment as a “priority” user.
Nevertheless, downloading data via a Wi-Fi connection should currently run at 25 to 220 Mbps. Uploading is usually slower and is specified with a transfer rate of between 5 and 20 Mbit/s. However, a consistently uninterrupted connection is excluded. The actual transfer rate may also be slower.
For the most part, however, the typical bandwidth during peak usage times is a good 90 Mbit/s. Gigabit Internet customers can only laugh about this, but households whose broadband connection may still be years away from being implemented could at least find a temporary solution here.
Please note: Although online games are generally possible, comparatively high latencies of 40 milliseconds upwards and occasional disconnections could cloud the experience unpredictably.
Starlink: Pros and cons
Starlink offers some advantages in terms of accessibility, but on closer inspection it also has quite a few disadvantages. We have compiled a list of these in the following section:
Key advantages of the technology
- Remote areas can be supplied with internet
- Upgrading the infrastructure in places with weak connections
- More fail-safe in the event of natural disasters, provided there is electricity
- Fleet transportation of compact satellites into space possible
- Material-saving compared to the large-scale installation of radio masts
These are the disadvantages of the service
- Additional peripherals cause additional costs
- Latency not at the level of other broadband providers
- Transportation into space increasingly causes space debris
- Negative impact on weather forecasts
- Light pollution in the night sky
- No real global coverage yet
- Limited capacity can cause speed bottlenecks
- Stable connection not guaranteed throughout
- Usually has to be installed outside
Why is Starlink problematic?

The project is by no means uncontroversial and has raised questions and discussions on various topics right from the start. Astronomers are critical of the project, for example, as Starlink is said to make it more difficult to observe stars and asteroids.
The reason for this is the high reflectivity of the satellites, which can often be higher than that of other celestial bodies and therefore represents light pollution, so to speak. The company is already actively intervening here and is trying to minimize this problem by taking measures to reduce the brightness of the satellites during operation.
Impairment of weather forecasts

Meteorologists and climate researchers have concerns about inaccurate weather forecasts, as the Starlink signal from a terminal appears as a bright dot on weather maps. However, this observation usually indicates an accumulation of a lot of water vapor. This makes it difficult to make a clear classification and can have a negative impact on the forecast.
Reliable forecasts are made even more difficult as a result of this problem. In extreme cases, the regions in question would have to be excluded from weather measurements and a loss of data would have to be accepted. This is obviously not in the interests of research.
Increased collision risk and Kessler effect feared
Increasing space debris further increases the risk of collision. According to the Chinese government, the Tiangong space station has already had to correct its course around the Earth several times to avoid Starlink satellites, even though the terminals are equipped with technologies that enable the celestial bodies to avoid collisions on their own.
The space agency NASA is already concerned about the safety of space travel and warns that the risk of collisions is constantly increasing and that a chain reaction, the so-called “Kessler syndrome“, named after the astrophysicist Donald J. Kessler, could occur.
While the concept also provides for satellites to burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere at the end of their service life in an orderly manner and with virtually no residue, the real problem lies in the many rocket launches required to transport the technology.
Although some reusable solutions are used here too, components such as rocket stages remain in space. Even after many years, fuel residues can lead to an explosion and generate further particles that orbit uncontrollably around our planet.
Technical data on the Starlink satellites
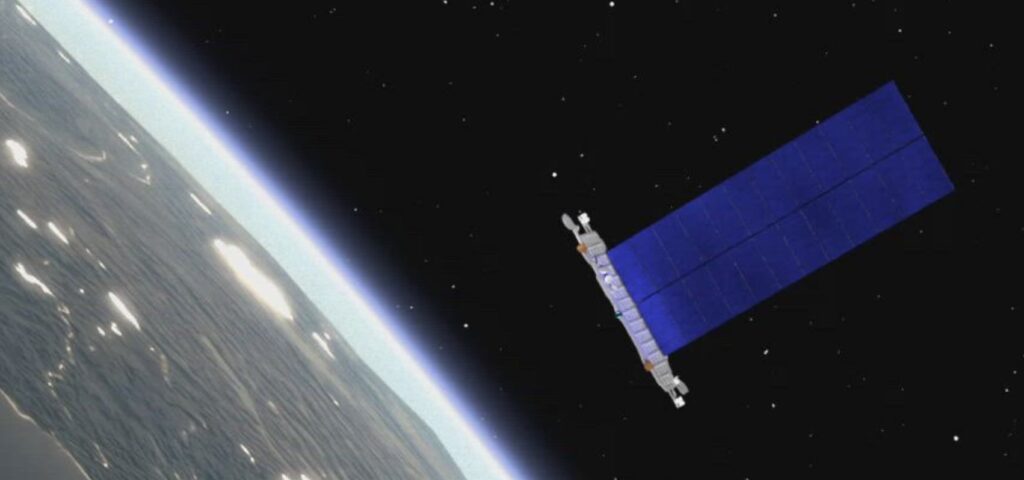

| Model | Version 0.9 | Version 1.0 | Version 1.5 | Version 2.0 Mini |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mini weight | 227 kg | 260 kg | approx. 300 kg[ | approx. 800 kg |
| Power supply | Solar panel | Solar module | Solar module | Solar module |
| Capacity | – | 18 GBit/s | – | 100 GBit/s |
| Communication | Ku-band | Ku-band Ka-band | Ku-band Ka-band Laser inter-satellite links | Ku-band Ka-band Laser inter-satellite connections LTE |
| Actuator | Hall drives with krypton gas | Hall drives with krypton gas | Hall drives with krypton gas | Argon Hall thrusters |
| Incandescence on re-entry | up to 95 % | up to 100 | up to 100 | up to 100 |
Starlink in the future: what are the prospects?
By 2027, the already extensive network is set to grow by over 6,000 more satellites to a total of 12,000 units stationed in space. It remains to be seen whether this will also have an impact on the practical bandwidth and whether we will be able to regularly access gigabit connections via Starlink in a few years’ time. The decisive factor will be the development of demand until then.
Irrespective of this, 30,000 satellites have already been applied for (as of January 2024). The flood of supply for the rest of the decade and probably the coming decade is therefore unlikely to stop for the time being. As already mentioned, many other nations are on the Starlink waiting list and are expected to be connected to the network this year and in the coming years in order to further increase global availability.
From the end of 2024, the company is also planning to launch a much larger concept in the form of the third generation of satellites into orbit using the large Starship rocket. By then, the issue of space debris should also be a thing of the past – at least at this point. The reason for this is the completely reusable design of the rocket.
Frequently asked questions about Starlink
How can I order Starlink?
To order Starlink, visit the official Starlink website. There you can check if the service is available in your area and order the Starlink kit directly.
What is included in the Starlink kit?
The kit includes the Starlink antenna for reception, a WLAN router for signal scattering, a power supply unit, additional cables and a mounting stand.

Can Starlink be used in homes?
A relatively clear no at this point! A complete view of the sky must be guaranteed so that the Starlink antenna can follow the satellite signal without restriction if required.
How long does it take to deliver Starlink?
The delivery time can vary considerably. In many cases, however, you will receive your order at home within a month.
Where should Starlink be installed?
An installation with a clear view of the sky is important. Outdoor areas are therefore preferred. Many different mounts are available for this purpose.
Why is a clear view necessary?
Objects such as trees, awnings or canopies can interfere with the signal and cause interruptions. An obstacle-free path is therefore very important for a smooth connection setup.
How do I know if a roof installation is necessary?
The Starlink app helps to check the visibility conditions and thus clarifies in which area largely uninterrupted operation is possible.
How do I download the Starlink app?
The utility program is available in the App Store for iOS-based devices and in the Google PlayStore for Android devices and can be downloaded from there free of charge.
Can Starlink be installed on my motorhome or camper?
Yes, a special version including a suitable subscription is available for this purpose. This means you don’t have to do without an internet connection or tap into your mobile data volume when traveling.
What data limits does Starlink have?
All subscription models are currently sold without strict data limits. However, depending on further developments, this could change in the future. You also have the option of booking a quota of so-called “priority data” for certain tariffs.
Do I have to pay a deposit for Starlink?
Yes, a deposit is required to pre-order Starlink. This deposit will be deducted from the cost of the starter package if the order is continued. In the event of cancellation, the deposit will be refunded within a certain period of time.
Where can I cancel my Starlink order afterwards?
Cancellations are generally possible via the customer portal on the Starlink website. After registering, you can cancel your pre-order there and receive your deposit back within ten days.
How can I cancel Starlink?
To cancel your Starlink subscription, you must log in to the Starlink website and select the “Cancel service” option. After canceling, your internet will remain active until the end of the current billing cycle, but a partial refund of the subscription is not possible.
Where can I see Starlink satellites in the sky?
To see Starlink satellites in the sky, you can use websites or apps like “Heavens-Above” or “Find Starlink“, which will show you times and directions for visibility in your area. Choose a viewing location with little light pollution and a clear view of the sky. The satellites are most visible just after sunset or before sunrise, when they are strung along the sky like a string of pearls.